NI-SPAN-C® alloy 902
| 牌号 | NI-SPAN-C® alloy 902 |
| 厂家 | Special Metals Corporation |
| 分类 | Nickel |
| 介绍 | Most metals and alloys have a negative temperature coefficient of modulus of elasticity; that is to say they lose stiffness when heated. They also have a positive coefficient of thermal expansion, increasing in length when heated. These two effects are due to increase in energy of the atoms with increase in temperature. Some ferromagnetic materials, however, exhibit markedly different behavior, which can be utilized to design constant modulus alloys. The modulus of elasticity € of ferromagnetic materials is a complex function of a number of physical properties, related by the adjacent equation. Each of the factors ?, µ and k is affected by composition, strain and temperature. In order that the modulus of elasticity will remain constant with variation in temperature it is necessary to select a composition for which ?²µ changes at the same rate and in the same direction as k². The same constants are also sensitive to applied magnetic fields so that the modulus of elasticity changes with a change in magnetic field strength. As these considerations apply only to ferromagnetic materials they do not hold when an alloy has been heated beyond its Curie temperature, the point at which it changes from ferromagnetic to paramagnetic behavior. |
| Special Metals Corporation 产品展示 | 种类 |
|---|---|
| Inconel® alloy 718 | Nickel |
| Inconel® alloy 601GC® | Nickel |
| Inconel® alloy MA758 | Nickel |
| Monel® alloy 400 | Nickel |
| Nickel 212 | Nickel |
| Nitinol Chrome-Doped Superelastic Ni-Ti Alloy | Nickel |
| INCOTHERM® alloy TD | Nickel |
| NIMONIC® alloy 90 | Nickel |
| INCOLOY® alloy 907 | Nickel |
| Inconel® alloy 686 | Nickel |
订购说明
上海松翰塑化科技有限公司订货流程
【订购导引】
我司所销售所有产品均为原厂原包,均可提供相关资料报告(如:物性表,MSDS报告,UL报告,COA报告,SGS报告,FDA等)!
如您需要提前了解原料产品的相关性能或是需要原料产品的相关报告,请您通过电话或是客服QQ与我联系!
【物流说明】
自接到贵司订购单24小时内发货,珠三角,长三角,北京,天津均支持代收货款。货物送达后,请第一时间检查外包装,如发现物流过程中出现大量包装损坏及原料外漏的,请让物流人员出具证明并保存,并在24小时内与我司客服部取得联系。
【订购流程】
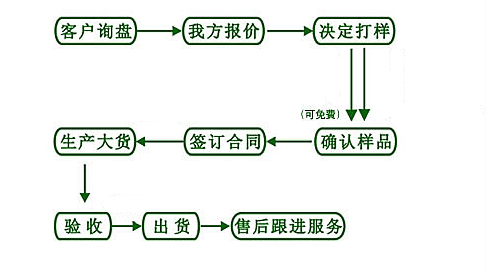
【退换货处理】
退货:
依照中华人民共和国消费者保护法规,在您收到货品7天内,若发现您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,您可以要求退货,请主动与本公
司联络,敝公司接到您的商品之后,会将您的购物金额全额退回。
换货:
若您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,请您于7天内与本公司联络,本公司有专人处理换货事宜。
我司所销售所有产品均为原厂原包,均可提供相关资料报告(如:物性表,MSDS报告,UL报告,COA报告,SGS报告,FDA等)!
如您需要提前了解原料产品的相关性能或是需要原料产品的相关报告,请您通过电话或是客服QQ与我联系!
【物流说明】
自接到贵司订购单24小时内发货,珠三角,长三角,北京,天津均支持代收货款。货物送达后,请第一时间检查外包装,如发现物流过程中出现大量包装损坏及原料外漏的,请让物流人员出具证明并保存,并在24小时内与我司客服部取得联系。
【订购流程】

【退换货处理】
退货:
依照中华人民共和国消费者保护法规,在您收到货品7天内,若发现您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,您可以要求退货,请主动与本公
司联络,敝公司接到您的商品之后,会将您的购物金额全额退回。
换货:
若您收到的商品有瑕疵或损坏,请您于7天内与本公司联络,本公司有专人处理换货事宜。